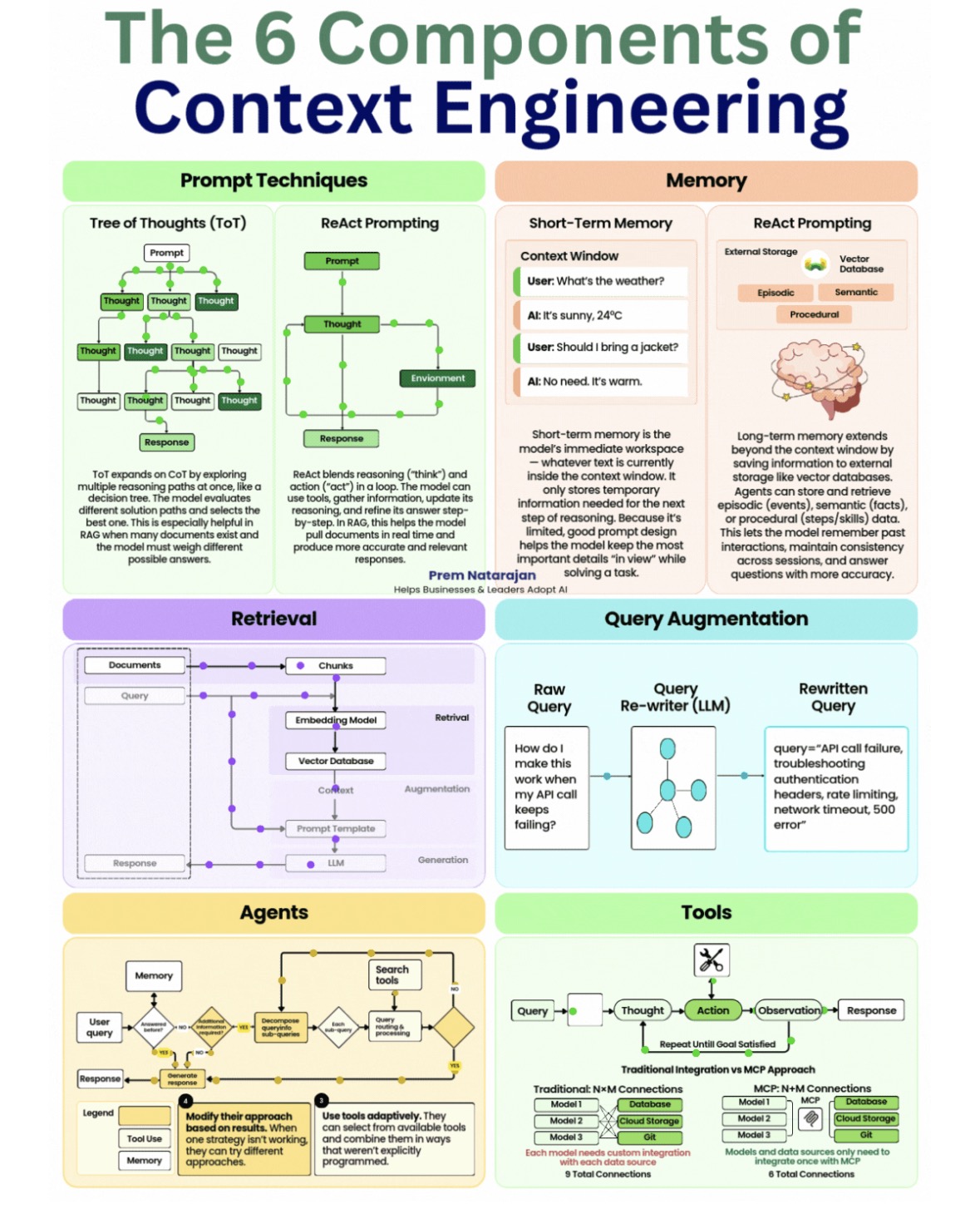
An "Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI)" course typically bridges the gap between theoretical AI concepts and real-world implementation. These courses are designed to teach students not just how AI works, but where and why it is used to solve practical problems across various industries.
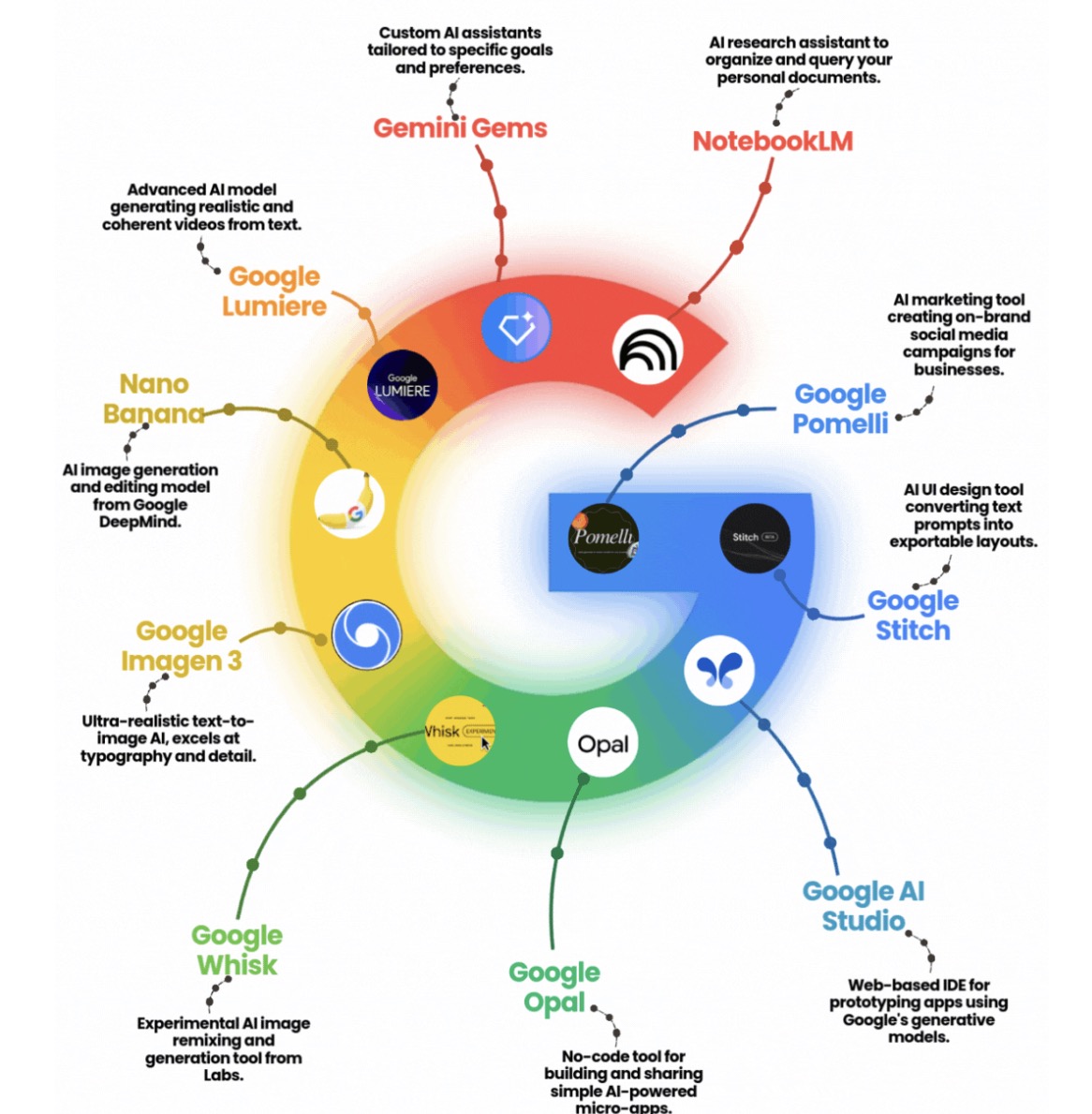
Depending on the target audience, these courses usually fall into one of two categories:
-
Technical/Developer Track: Focuses on coding, algorithms, and building models (e.g., "How to build a face recognition system").
-
Business/Strategy Track: Focuses on use cases, ROI, and integration (e.g., "How to leverage AI for supply chain optimization").
Below is a comprehensive summary of a standard "Applications of AI" course syllabus, blending both perspectives.
Course Objectives
-
Understand Core Concepts: Grasp the fundamentals of Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Neural Networks.[1]
-
Identify Opportunities: Learn to spot problems in healthcare, finance, and industry that can be solved with AI.[2]
-
Implementation: Gain hands-on experience with tools (Python, TensorFlow) or strategic frameworks for deploying AI solutions.
-
Ethics & Society: Analyze the ethical implications of AI, including bias, privacy, and job displacement.
Typical Course Syllabus Structure
Module 1: Foundations of AI & Machine Learning
-
What is AI? Narrow AI vs. General AI, history, and current state.
-
Machine Learning Basics:
-
Deep Learning Intro: Neural networks, backpropagation, and why "Deep" Learning is driving the current AI boom.
Module 2: Natural Language Processing (NLP)
-
Concept: Teaching computers to understand and generate human language.
-
Applications Covered:
-
Chatbots & Virtual Assistants: Automated customer support (Siri, Alexa, customer service bots).
-
Sentiment Analysis: Analyzing social media to gauge brand reputation.
-
Language Translation: Real-time translation services (Google Translate).
-
Generative AI (LLMs): Understanding how models like GPT-4 work for content creation and summarization.
-
Module 3: Computer Vision
-
Concept: Enabling computers to "see" and interpret visual data from the world.
-
Applications Covered:
-
Healthcare: analyzing X-rays and MRI scans to detect tumors earlier than human doctors.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Object detection (identifying pedestrians, stop signs, and lane markers).
-
Security: Facial recognition systems and anomaly detection in surveillance feeds.
-
Manufacturing: Visual quality control (spotting defects on an assembly line).
-
Module 4: AI in Business & Industry
-
Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to forecast future trends (e.g., stock market prediction, demand forecasting).
-
Recommendation Systems: How Netflix and Amazon suggest movies and products (Collaborative Filtering).
-
Fraud Detection: Spotting unusual patterns in banking transactions in real-time.[7]
-
Robotics: Automating physical tasks in warehousing (Amazon Kiva robots) and agriculture.
Module 5: Generative AI & Creative AI
-
Image Generation: Tools like Midjourney or DALL-E for design and marketing.
-
Code Generation: Using AI assistants (like GitHub Copilot) to accelerate software development.
-
Synthetic Data: Creating fake data to train models when real data is scarce or private.
Module 6: Ethics, Policy, and Governance
-
Bias and Fairness: Case studies where AI discriminated against certain groups (e.g., biased hiring algorithms).
-
Explainability (XAI): The "Black Box" problem—understanding why an AI made a specific decision.
-
Future Trends: Regulation, safety, and the impact of AI on the future of work.
Tools & Technologies Often Taught[1][3][4][8][9][10][11][12]
-
Programming Languages: Python (industry standard), R.
-
Libraries: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-Learn, Keras, OpenCV (for vision), NLTK/Spacy (for text).
-
Platforms: Google Colab, Jupyter Notebooks, AWS SageMaker, Azure AI.
Common Capstone Projects
Students often complete a final project to demonstrate their skills. Examples include:
-
Spam Classifier: Building a model to automatically filter emails.
-
House Price Predictor: Using regression to estimate real estate values based on features like square footage and location.
-
Disease Detection: Training a model to identify pneumonia from chest X-ray images.
-
Stock Sentiment Analyzer: Scrape financial news to predict if a stock will go up or down.
Google Search Suggestions
- Teacher: niepa User

